- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
What is the Difference Between Pulse Oximeter and Pulse Oximetry?
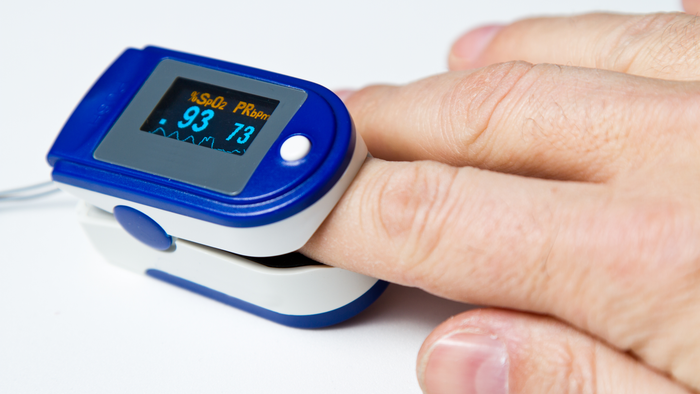
When discussing healthcare tools and procedures, terms often get interchanged, leading to confusion. Two such terms are “pulse oximeter” and “pulse oximetry.” Despite their close relation, they refer to different concepts within the realm of medical diagnostics. This article delves into their distinctions and applications, clarifying how each plays a crucial role in monitoring patients’ health.
Table of Contents
Understanding Pulse Oximetry
Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive method used to measure the oxygen saturation level in the blood. It provides critical information about a person’s respiratory function and the efficiency of oxygen transportation to different parts of the body. By monitoring blood oxygen levels, healthcare providers can detect issues like hypoxemia, which can be indicative of respiratory or cardiovascular problems.
The Mechanics of Pulse Oximetry
Pulse oximetry works by utilizing a sensor that emits light wavelengths through a body part, usually a fingertip or earlobe. The sensor measures the amount of light absorbed by oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin in the blood. This absorption data is then processed to calculate the oxygen saturation percentage, providing a quick and accurate assessment of a patient’s oxygen levels.
Introduction to Pulse Oximeters
A pulse oximeter is a small, portable device used to perform pulse oximetry. These devices have become increasingly popular due to their ease of use, non-invasiveness, and the critical data they provide. Pulse oximeters are commonly used in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and even at home, particularly for patients with chronic respiratory conditions.
How Pulse Oximeters Work
Pulse oximeters consist of a probe and a processing unit. The probe, which is placed on a body part like a finger, contains light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and a photodetector. The LEDs emit light at specific wavelengths that pass through the tissue and are absorbed differently by oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. The photodetector captures the light that emerges from the tissue and sends the data to the processing unit. The processing unit then calculates the oxygen saturation level and displays it on the screen.

Key Differences Between Pulse Oximetry and Pulse Oximeters
While pulse oximetry refers to the process of measuring blood oxygen levels, a pulse oximeter is the device used to perform this measurement. In other words, pulse oximetry is the technique, and the pulse oximeter is the tool. Understanding this distinction helps in appreciating the specific roles each plays in health monitoring.
Clinical Applications of Pulse Oximetry
Pulse oximetry is widely used in clinical settings to monitor patients’ oxygen levels during surgery, in intensive care units, and in emergency situations. It is also crucial for managing chronic respiratory diseases such as COPD and asthma. By continuously monitoring oxygen saturation, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about patient care and treatment.
The Role of Pulse Oximeters in Home Health Monitoring
With the rise of telemedicine and home healthcare, pulse oximeters have become valuable tools for patients managing chronic conditions at home. These devices allow individuals to monitor their oxygen levels regularly, providing data that can be shared with healthcare providers remotely. This continuous monitoring helps in early detection of potential health issues and timely intervention.
Technological Advances in Pulse Oximetry and Pulse Oximeters
Advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated pulse oximeters with additional features such as Bluetooth connectivity, data storage, and integration with mobile health apps. These enhancements have made it easier for both patients and healthcare providers to track and manage health data effectively.
Importance of Accuracy and Calibration in Pulse Oximeters
The accuracy of pulse oximeters is paramount, especially in clinical settings where treatment decisions are based on the readings provided. Regular calibration and maintenance of these devices are essential to ensure they provide accurate and reliable data. Healthcare providers should be aware of the factors that can affect the accuracy of pulse oximeter readings, such as poor circulation, skin pigmentation, and external light interference.

Future Directions in Pulse Oximetry
The future of pulse oximetry looks promising with ongoing research and development aimed at improving the accuracy, usability, and affordability of pulse oximeters. Innovations such as wearable pulse oximeters and advanced algorithms for data interpretation are expected to enhance the utility of these devices in both clinical and home settings.
Conclusion
In summary, while pulse oximetry and pulse oximeters are closely related, they refer to different aspects of measuring blood oxygen levels. Pulse oximetry is the technique, and pulse oximeters are the devices used to perform this measurement. Both play critical roles in healthcare by providing essential data for monitoring respiratory function and ensuring effective patient care. Understanding their differences and applications can help in better utilizing these tools for optimal health outcomes.

